Medical Research and Reliability
The medical industry requires reliable products that help save lives and keep patients healthy. Whether it is a surgical instrument or a post operation application, we can supply it.
Below you can see our product lines that cater to the industry and the applications of our products in the medical industry.
Product Lines
Arch Wire: Arched, sturdy, thin wire often used as the main support for braces.
Ligature Wire: Small connective bands attaching brackets to arch wires.
Braiding wire is round wire in a braided arrangement, helping ensure tubes don’t kink, and that devices like catheters don’t fail under pressure.
Custom cable assemblies crafted with precision and expertise. Our aircraft, military, and commercial cable assemblies are all highly customizable, and are durable enough to withstand demanding applications.
Guidewires are thin metal tubes used to guide linear objects (needles, tubes) through confined structures (blood vessels) or in environments involved in treating other organs with fluids.
Core wire is a single end wire used as a mandrel, or place holder during medical tubing extrusion processes. Once the tubing polymer is extruded, the core wise is elongated to decrease the wire’s diameter. Once the wire is slid out of its “sheathing”, it leaves a round tube for medicine delivery, device insertion or other technical uses.
Staples: Metal clips used to keep wounds shut. Less precise than sutures but offers faster application.
Sutures: Wire threaded through a needle to keep wounds shut. More precise wound closure, suitable for delicate or smaller incisions.
Other Relevant Products From Our House of Brands:
Many of our products can be used as a type of medical wire. Whether used in a surgical procedure, to keep hospitals clean and safe, or to close a wound, our products remain the right choice.
Here are the various medical applications that use Central Wire product:
Product Applications

Antimicrobial Uses
Stethoscopes: Copper is used in stethoscopes both for acoustic transmission, as it is an excellent conductor of sound, but also to help inhibit the growth of bacteria on the surface of the stethoscope.
Bed Rails/Tables: Copper’s antimicrobial qualities make it an ideal material for surfaces around hospital beds, to kill bacteria potentially being transmitted by the patients. These high-touch surfaces and materials within hospitals often use copper wire to avoid spreading bacteria or microbials among sick patients and hospital employees.
Endoscopics
Endoscopy is the insertion of a long, thin tube directly into the body to observe an internal organ — such as the gastrointestinal tract — in detail.
Strong, flexible wires can be used in endoscopic procedures for added functionality in examining hard to reach organs and other areas.

Implantable Uses
Pacemakers: Copper is used in the leads that connect the device to the heart, due to its conductivity and biocompatibility.
Defibrillators: Often used in the wiring and connectors within the internal circuitry of the defibrillator due to its conductivity.
Neurostimulators: Copper is used in the leads that deliver electrical stimulation to specific nerves or regions of the brain. Copper wire can be used in these implantable medical devices because copper is biocompatible. Copper wire provides the precises electrical connections required while keeping the patient safe.
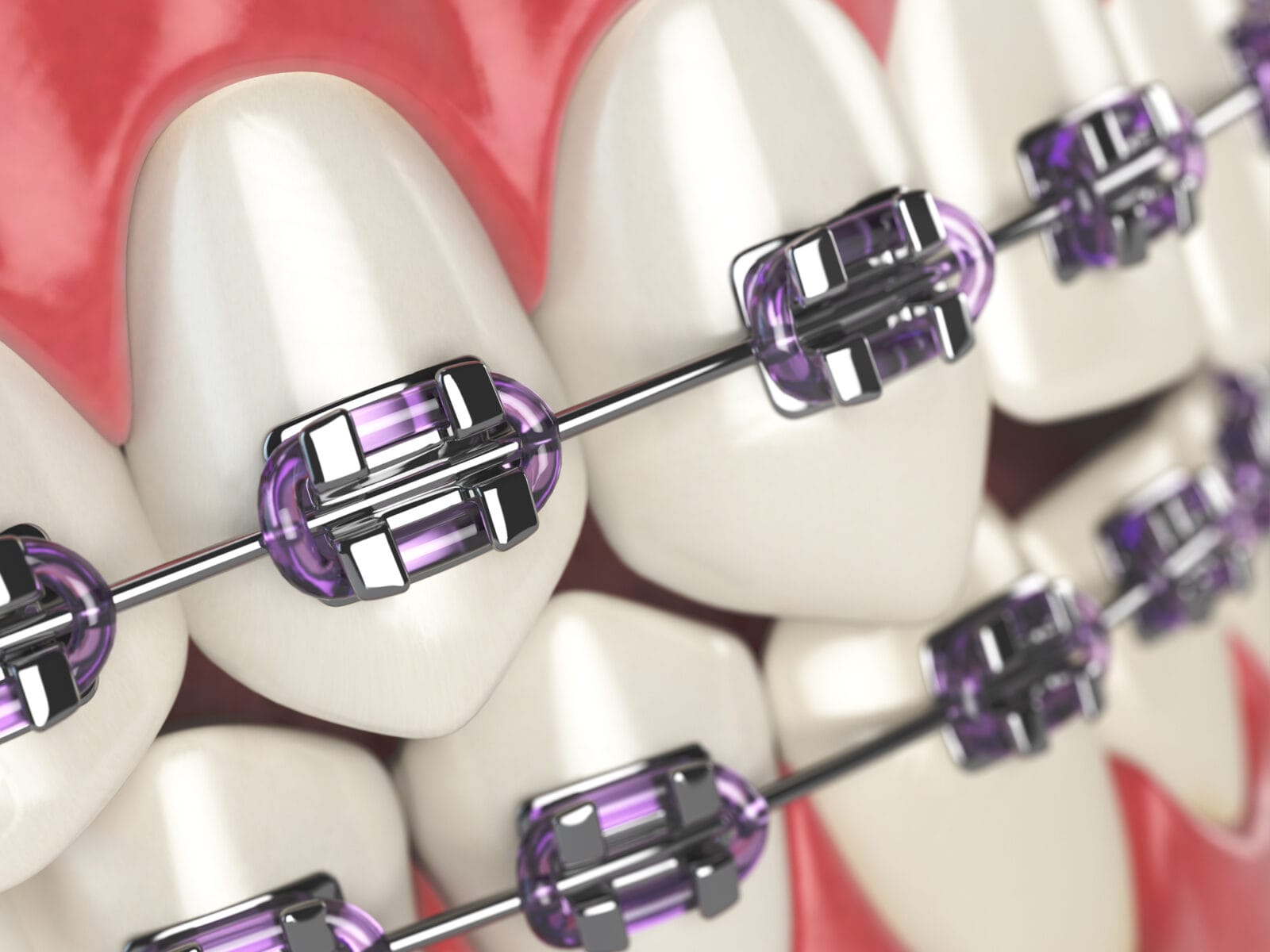
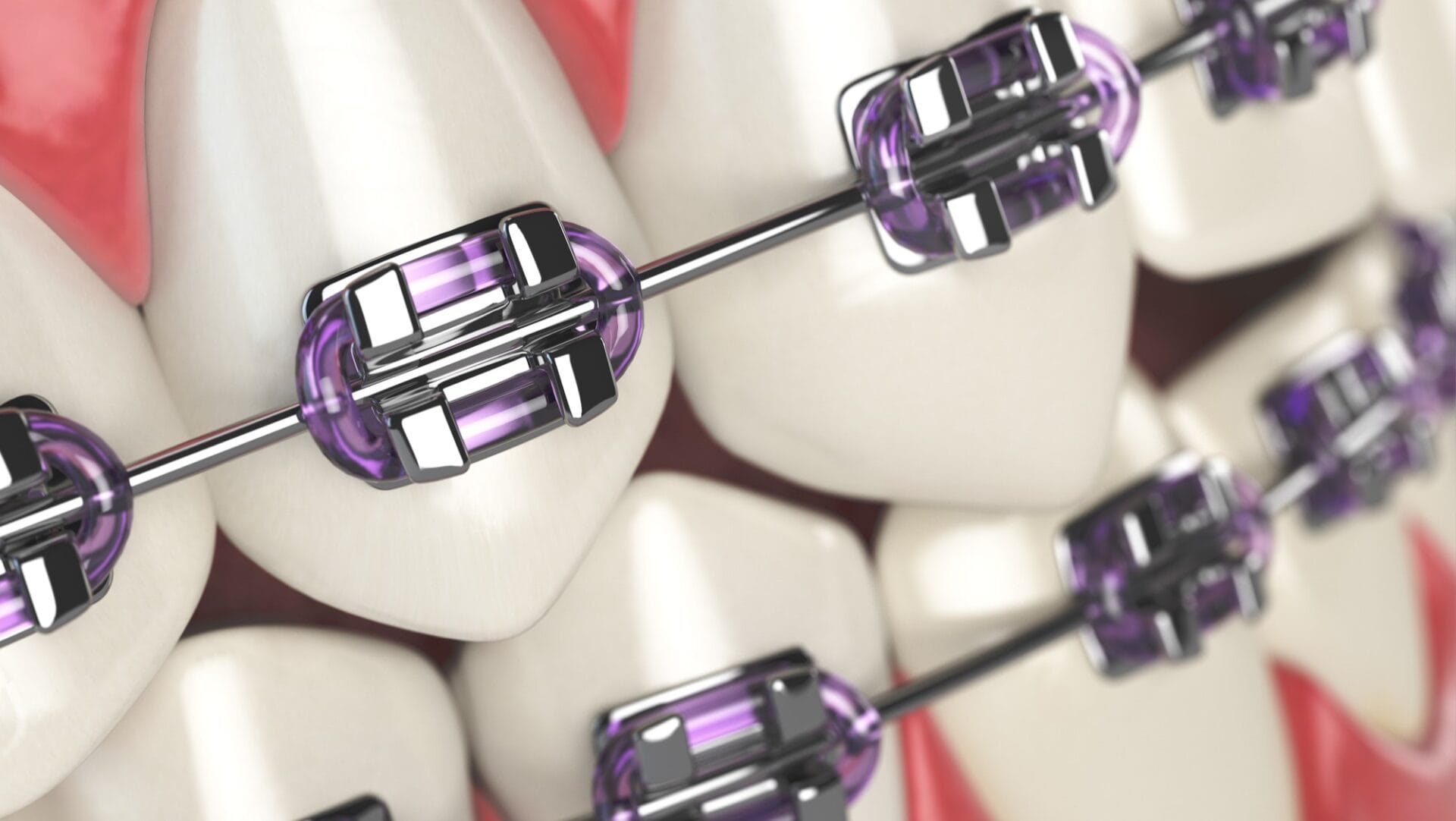
Orthodontics
Orthodontics is a dental specialty focused on aligning your bite and straightening your teeth. Braces use both arch wire and ligature wire to keep teeth in place and slowly begin to straighten them.
Arch wire runs across the teeth, through brackets, constantly pulling teeth back into position. Ligature wire is tiny rubber bands that tie brackets and arch wires together.
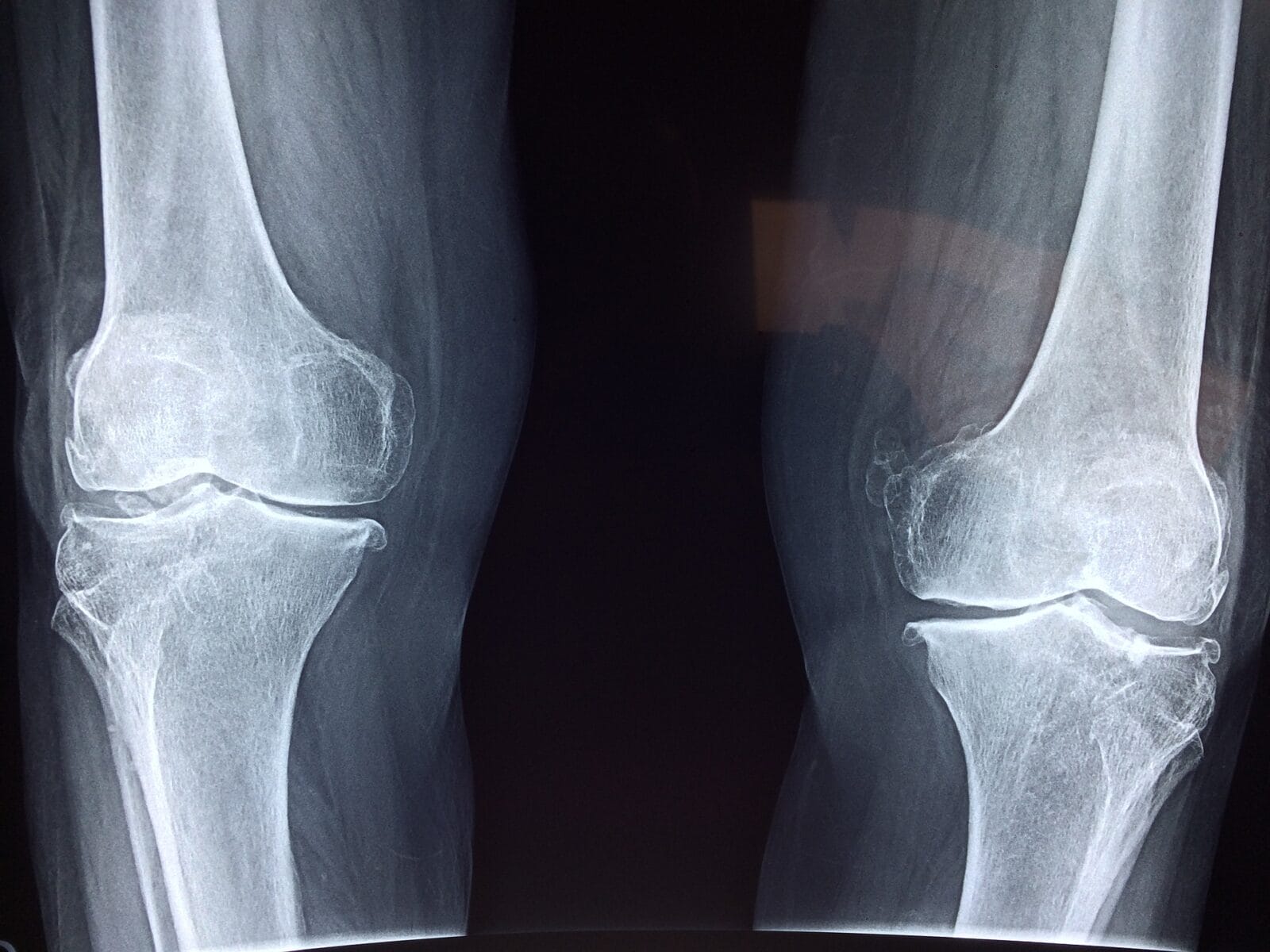
Orthopedics
Cerclage cable: Type of orthopedic fixation wire placed to approximate fractured bone fragments
Pins: Used to hold damaged or broken bones in position until they are healed.
Spinal rods: Spinal rods are used as support during spinal fusion surgery, to hold bones together before they eventually fuse together as one.
Fixation wire/cables: Same application as pins, just using wire instead of pins to support and help heal broken bones.
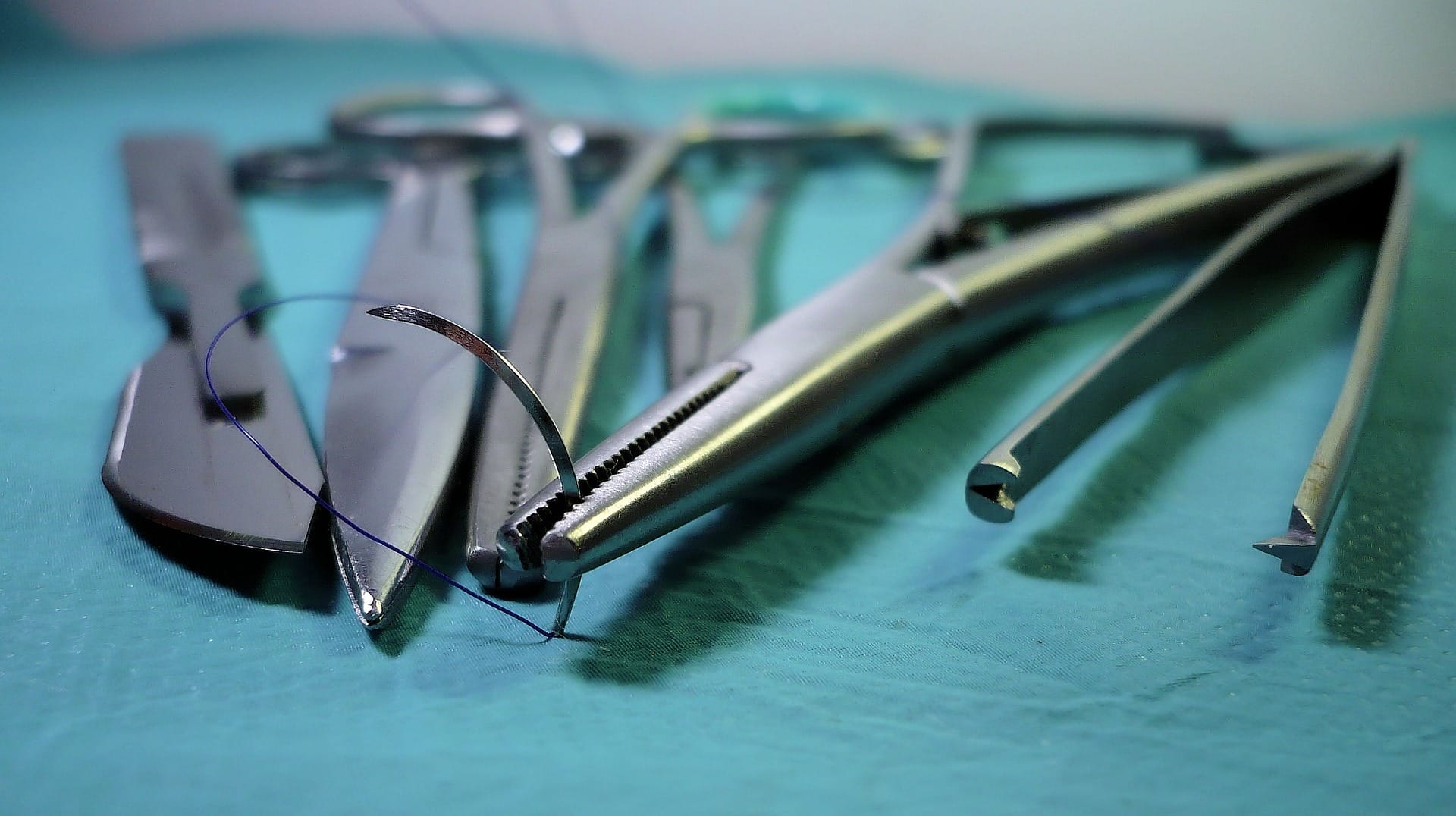
Surgical Closures
Suture wire: Used to hold body tissues together after an injury or surgery, suture wire is generally threaded with a needle to stitch wounds shut
Staple wire: Like the use in stitches, staple wire keeps staples shut to close wounds. Staples are used instead of sutures to reduce the local inflammatory response, reduce the width of the wound, and shorten the time it takes to close.

Surgical Instruments
Dental explorers: A sharp probe used in dental inspection to determine the presence of caries, enamel, dentin defects and more.
Needles: Fine wire used in needles to apply vaccinations, medicine etc. through the syringe into the body.
Gigli saws/bone saws: A flexible wire saw used for bone cutting in surgeries, often specifically for amputations when exact cuts are needed.
Periodontal probes: Thin dental tool used to discover periodontal pockets, which are openings between the teeth and gum line, and often signs of gum disease.
Retrieval forceps: Thin tool used for the retrieval of catheter tubing, wire guides, or other foreign objects from the vascular system.
Vascular Uses
Catheters: Tube inserted into the bladder allowing fluids to drain freely. Guidewires help navigate catheters through blood vessels around these organs.
Angioplasty procedures: Procedure using fine wire to open blocked coronary arteries which often causes disease.